
As search experiences continue to evolve, one thing is clear: content that gets pulled into AI-generated responses isn’t just optimized—it’s intelligently structured, deeply authoritative, and incredibly human-centric.
Implementing effective AI SEO strategies is crucial in this landscape. AI search tools like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and Microsoft’s Copilot, as well as Perplexity, Claude, and ChatGPT, prioritize clear, well-organized content from trustworthy sources. But building AI-friendly content doesn’t mean writing for machines. It means engineering your content so it works for both people and algorithms—offering clarity, depth, context, and structure.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore what makes content AI-friendly (and thus more human-friendly), with practical examples across industries like lawn care, law, healthcare, accounting, consulting, and manufacturing. Whether you’re a CMO at a mid-market firm or leading digital strategy for a multi-location brand, these tactics will help your content earn presence in the AI knowledge graph—and command attention across the web.
Contents
- 1. Clear Structure and Purpose: Help AI and Humans Navigate with Ease
- 2. Schema Markup: Translate Content for AI Models
- 3. Location-Aware Media: Tag Images with Intent
- 4. Build Authority Through Triangulated Content
- 5. Authority Signals: Give AI a Reason to Cite You
- 6. Depth and Originality: Don’t Be Generic
- 7. Podcasting: Feed the Knowledge Graph at Scale
- 8. Internal Linking: Connect the Dots
- 9. Metadata and Accessibility: Small Things, Big Impact
- 10. Refresh, Update, and Monitor
- Final Word on AI SEO Strategies: Design for AI, Deliver for People
AI models rely on structure to determine how to interpret content. The same goes for human readers. A page without clear headers or logical flow creates confusion—and gets skipped.
Best Practices:
- Use proper heading tags (H1 for main title, H2s for subtopics).
- Start with a TL;DR or short summary for long-form content.
- Use bullets, callouts, and short paragraphs to aid scannability.
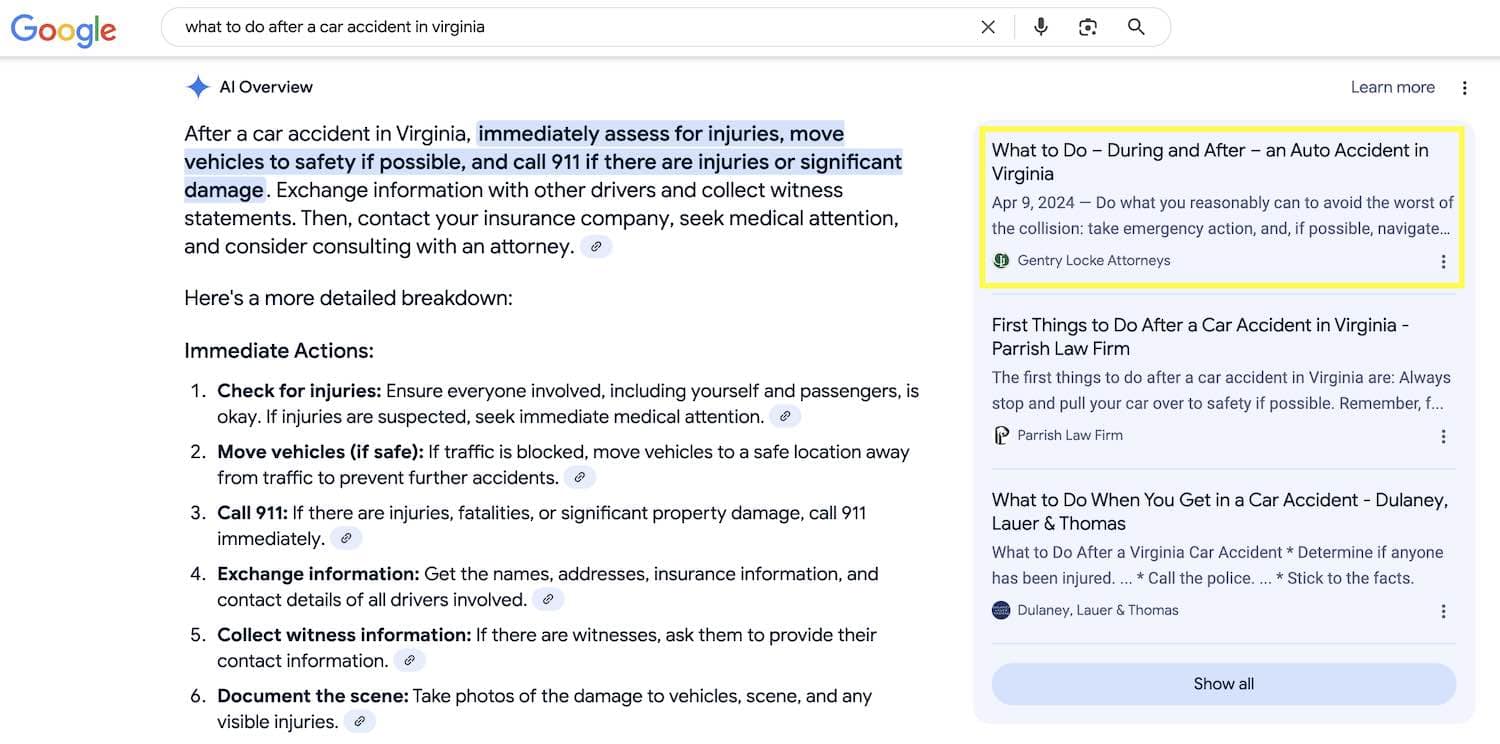
Industry Example: A law firm targeting accident cases in Virginia should write a guide like “What to Do After a Car Accident,” beginning with an at-a-glance checklist, then breaking the content into digestible sections like “When to Contact an Attorney,” “What Documents to Collect,” and “How Insurance Factors In.”
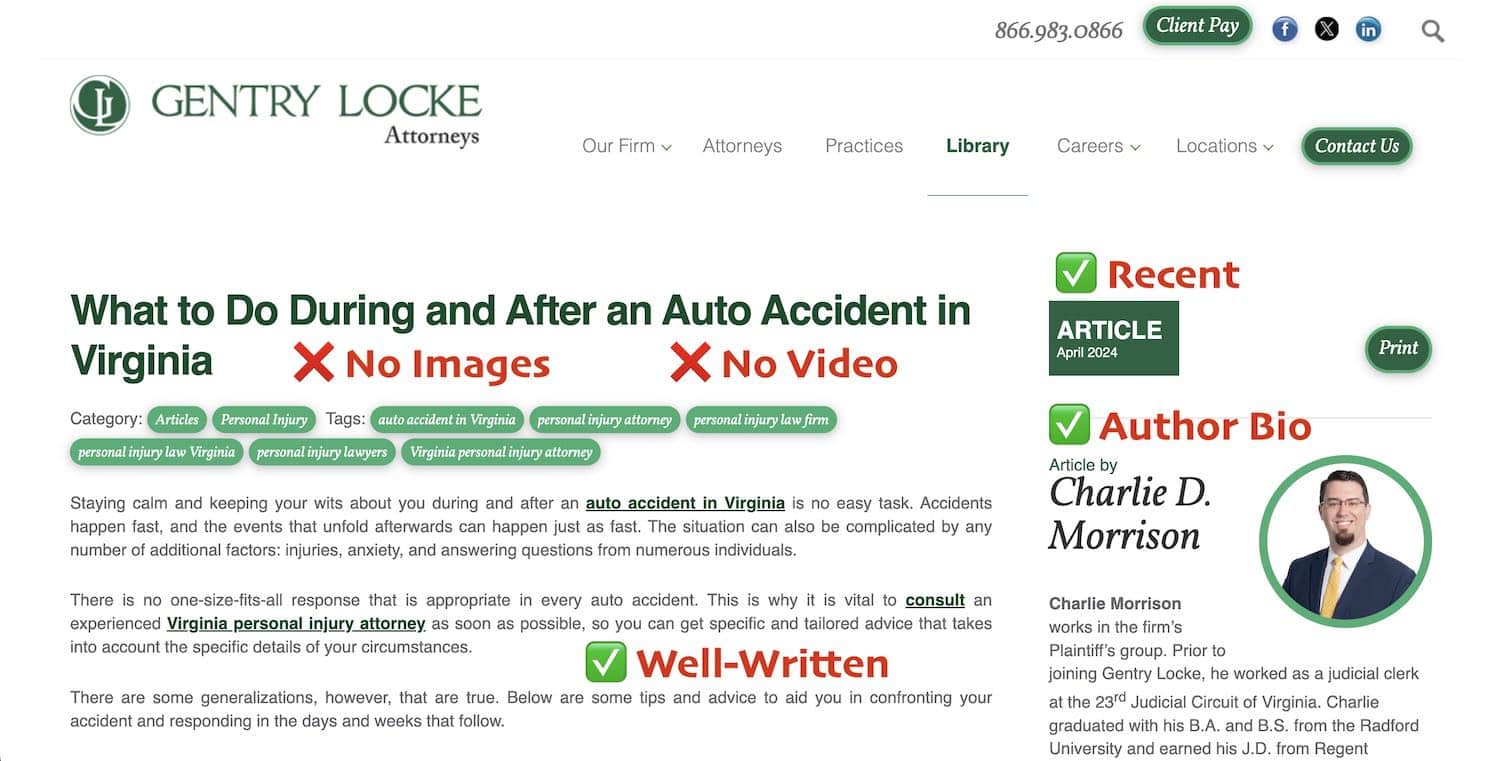
In the above example, Virginia law firm Gentry Locke Attorneys does a good job at tackling this approach. Someone who has been in a car accident and doesn’t know what to do might ask this question to Google or ChatGPT. While Gentry Locke was successful at achieving top citations in Google’s AI Overview for this article, they were not the top cited source in ChatGPT. Making some improvements to this article could help this firm solidify it’s position as the authority on this subject.
2. Schema Markup: Translate Content for AI Models
Schema is a type of code added to a website to explain what content is—not just what it says. It tells search engines and AI that a piece of content is a product, service, video, article, review, or something else entirely.
Common Types:
LocalBusiness,Organization,Product,FAQ,Event,HowTo,ArticlePersonandAuthorschema to associate content with an expertBreadcrumb,VideoObject, andReviewschema for richer UX
Use Case: A multi-state lawn care franchise can apply LocalBusiness schema to every service location page, reinforcing location-specific visibility. Pairing this with FAQ and ImageObject schema creates a multi-layered understanding for AI.
How to Check the Schema Markup of a Webpage:
If you want to quickly see what schema markup is applied to a webpage, just copy the URL and paste it into Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator. These free tools will show you exactly what structured data is present and which types (like Article, LocalBusiness, FAQPage, etc.) are being used—no need to dig through source code.
3. Location-Aware Media: Tag Images with Intent
When AI scans a page, images are part of the signal—but only if they’re labeled correctly.
Pro Tip: Leverage EXIF Data. EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data is metadata embedded in images, including location coordinates, timestamps, device type, and more. If you upload photos taken on-site at a business location or event, preserving this data can serve as proof of presence in that geography.
Example: A landscaping franchise showcasing work in Dallas should upload authentic photos taken in the field, preserving EXIF GPS metadata to support local content. This supplements ImageObject schema and signals legitimacy.
Even better: EXIF data isn’t locked in at the time the photo is taken—you can append or edit it after the fact using free tools like ExifTool or online EXIF editors. If you’re a Mac user, you can edit EXIF data in the Photo App. This means your team can enhance older images or stock photos by embedding metadata that reinforces relevance to a specific location or event, aligning visuals more tightly with your content strategy.
Also:
- Use structured filenames (e.g.,
lawn-treatment-dallas-spring2025.jpg). - Add descriptive alt text (e.g., “Team applying fertilizer on residential lawn in Dallas, TX”).
4. Build Authority Through Triangulated Content
Authority is not declared—it’s earned through consistency across platforms. When a Subject Matter Expert (SME) publishes insights in long form and echoes those insights across channels, it sends a powerful signal to AI models and human readers alike.
The Triangulation Strategy:
- Long-Form Thought Leadership on LinkedIn, Medium, or Substack (explains the big picture).
- Short-Form Takes and Commentary on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn (reactive, shareable).
- Website Articles tied back to the expert (structured and indexable).
The article linked below is one I originally published on Substack, where I explore the foundational thinking behind the strategies discussed here. It dives into the theories I developed before doing this work—the curiosity of AI, the subtle biases of its users, and the self-reinforcing nature of visibility in AI-driven search. While it’s written for a more reflective, inquisitive reader (and not necessarily intended to drive action), it plays an important role in my broader content ecosystem. Together with other pieces, it helps establish clear thought leadership and reinforces authorship across multiple platforms.
Industry Example: A consulting firm launching a proprietary transformation framework might:
- Post thought a leadership video on YouTube linking to their website.
- Publish a full breakdown on Substack.
- Publish a long form professional opinion piece on LinkedIn.
- Add a case study on their website with the YouTube video embedded.
- Share the SubStack and case study on company and personal LinkedIn profiles.
- Share quote cards from the videos across their social media channels.
Why it works: AI models prioritize verifiable sources. If your content spans formats, channels, and expressions—but consistently points back to the same individual or brand—it gets remembered.
5. Authority Signals: Give AI a Reason to Cite You
AI assistants look for signals of expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness (known as E-E-A-T). Human readers do the same.
Best Practices:
- Publish author bios with credentials, years of experience, and affiliations.
- Use
AuthorandPersonschema to attach content to real people. - Link to reputable third-party profiles (e.g., LinkedIn, publications, directories).
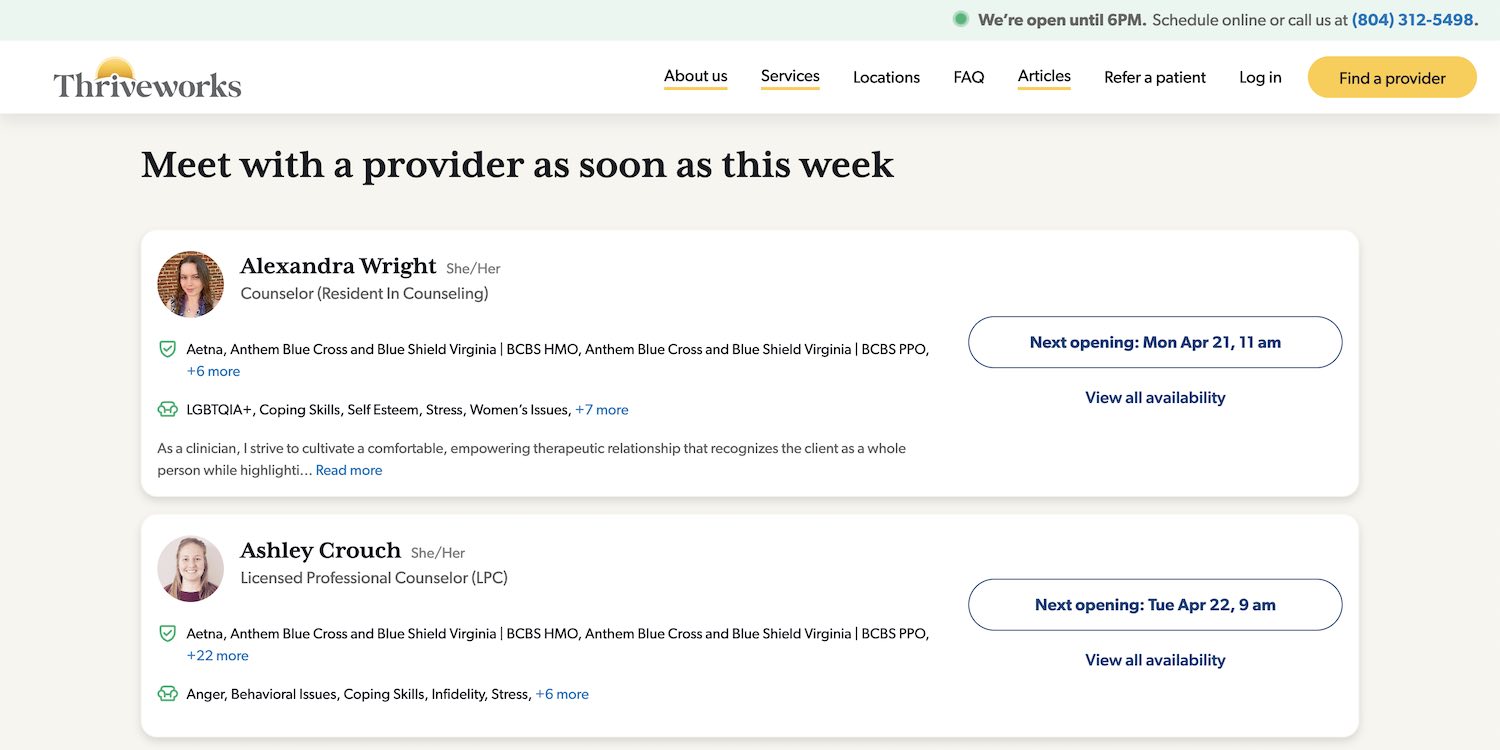
Industry Example: A mental health clinic publishing content on anxiety treatment should include bios for their licensed therapists or psychologists, link to their Psychology Today or state licensure profiles, and use schema markup to associate each provider with their specialties and certifications. This strengthens credibility and helps AI recognize the content as coming from trusted medical professionals.
The above example from Thriveworks appeared as a top cited source in AI overviews, leading me to include it as an example. However, the individual pages for each therapist do not actually use Schema markup. The marketing team here could go further to solidify its already strong position.
6. Depth and Originality: Don’t Be Generic
In the era of generative AI, regurgitated content has an extremely short shelf life. AI models don’t just retrieve—they synthesize. That means they’re trained to recognize patterns, filter noise, and elevate content that adds something new to the conversation. If your content simply echoes what already exists, it won’t stand out to humans—or AI.
The most effective content today goes beyond surface-level knowledge and dives into original insight, novel framing, and unique data that helps both readers and machines deepen their understanding of a topic.
Why Originality Matters
- AI favors distinct perspectives. Large language models are built to avoid repetition. When multiple sources say the same thing, they look for the one that explains it best—or the one with something extra.
- Original thinking creates citation gravity. Unique takes, proprietary frameworks, or new terminology you introduce can become anchors that AI returns to again and again.
- Novel content expands the knowledge graph. When you publish something that doesn’t already exist, you’re not just competing—you’re contributing to the intelligence layer AI references.
Ways to Stand Out:
- Create original graphics or illustrations. Avoid using the same stock visuals everyone else does. Diagrams that explain your own process or POV are far more valuable.
- Publish first-party data. If you run surveys, conduct internal research, or have usage patterns from your software or service, that data can make your insights unique and valuable.
- Document edge cases and exceptions. AI loves comprehensive answers. When you cover what others miss, you’re more likely to be featured in long-form answers or People Also Ask results.
- Share thought leadership or predictive takes. Forward-looking opinions on market trends, changes in user behavior, or strategic decisions can differentiate you from the pack.
- Offer use-case variety. Rather than a single scenario, provide multiple applications across industries or personas. It shows depth and relevance.
Example:
A B2B manufacturing company writing about CNC machining shouldn’t stop at “what it is.” To stand out:
- Include diagrams of machine components or tolerances for different materials.
- Embed time-lapse videos of parts being milled or finished.
- Highlight customer success stories from different verticals—how aerospace firms use ultra-tight tolerances vs. how automotive firms optimize for scale.
- Share common missteps or what design engineers often overlook when designing for CNC production.
Bonus Tip: Create Once, Cite Everywhere
A single, well-researched and well-structured piece of content can anchor multiple spin-off assets:
- Substack or Medium reflections expanding your thinking
- Slide decks or whitepapers shared on LinkedIn
- Snippets included in responses by AI models if well-linked and consistently referenced
By publishing original, insightful, and layered content, you not only serve your audience—you also shape what AI knows, trusts, and cites. It’s one of the few enduring ways to claim real estate in the attention economy without buying your way in.
This article is a spin-off from How to Optimize Your Website and Content to Rank in AI Search Results. I wrote it with the understanding that while explanation is helpful, it’s not enough on its own—especially when you’re trying to connect with a diverse audience of marketers. To be effective, you need to show what AI-friendly content actually looks like in different industries. That’s what this piece aims to do: go beyond the theory and offer real-world application.
7. Podcasting: Feed the Knowledge Graph at Scale
Podcasts are one of the richest formats for injecting long-form, natural language content into the web. They’re informal, unscripted, and authentic—exactly what AI models crave.
Why podcasts matter:
- They introduce spoken insights that mirror how people ask questions.
- With transcriptions, they become searchable and indexable.
- They can be segmented, quoted, and linked across platforms.
Example: An accounting firm might launch a podcast like “Finance in Focus,” where partners discuss tax deadlines, audits, and estate planning. These episodes can be:
- Transcribed and summarized into blog posts
- Embedded into service pages
- Pulled apart into short social clips with quotes and timestamps
Result: Dozens of content assets, all reinforcing domain expertise.
The above podcast episode is an example of a podcast we created to better explain the nuances of AI SEO strategies to our readers. We designed the podcast branding using Canva and Envato Elements, and we created the foundational episode with NotebookLM, Eleven Labs, and GarageBand, all within a few hours.
8. Internal Linking: Connect the Dots
AI doesn’t just crawl your site—it maps it. Every internal link creates a signal about how your content is structured, what topics are important, and which pages reinforce each other. Done well, internal linking helps generative AI and search engines understand your site’s thematic clusters and identify you as an authoritative source in your niche. It also improves navigation, keeps users engaged longer, and builds trust as they explore your expertise.
Think of your website like a city: pillar pages are landmarks, and internal links are the roads connecting everything. The more structured and purposeful those connections, the easier it is for both users and machines to understand the ecosystem you’ve built.
Best Practices:
- Link every blog post to at least one core service or pillar page. This strengthens your authority around key business offerings and helps distribute link equity across the site.
- Use descriptive, intent-rich anchor text. Instead of vague phrases like “click here,” use wording like “learn more about our tax planning strategies.”
- Add “further reading” sections and related content carousels at the bottom of blog posts and service pages to encourage deeper engagement.
- Update old content to link to new pages. Don’t just link forward—go back and integrate new resources into your legacy content to keep it relevant and improve crawlability.
- Maintain consistent URL structures and topic silos. Use category pages and hub-and-spoke content architecture to reinforce relationships between posts.
Use Case: A regional accounting firm offering audit, tax, and advisory services can publish an “Ultimate Guide to Financial Planning” as a top-level pillar page. This guide would link out to detailed sub-pages on topics like business structuring, depreciation schedules, charitable giving strategies, and end-of-year tax planning. Each of those sub-pages should then link back to the guide and cross-reference each other when relevant, creating a tightly connected cluster that helps AI recognize the firm’s comprehensive expertise in financial planning.
By thoughtfully interlinking your content, you build semantic clarity and topical strength—two critical signals AI uses to determine whether your content deserves to be cited in search results or AI-generated answers.
9. Metadata and Accessibility: Small Things, Big Impact
When content is structured well, it’s not just about what users read on the page—it’s also about how the page is presented elsewhere. Metadata and accessibility may seem like behind-the-scenes details, but together, they determine whether your content gets discovered, clicked on, and engaged with.
Metadata—including title tags, meta descriptions, and Open Graph (OG) tags—plays a vital role in how your pages appear in search results and social feeds. These elements affect click-through rates, preview content, and how platforms like Google and LinkedIn interpret your messaging. Well-crafted metadata can mean the difference between getting lost in the noise and being the first result someone clicks.
Accessibility ensures your content can be consumed by all users, including those using screen readers or navigating on mobile devices. AI and search engines also consider accessibility signals when evaluating content quality, making this not just an ethical imperative—but an SEO one as well.
Checklist:
- Write concise, compelling meta descriptions that reflect user intent and encourage clicks. Aim for ~150–160 characters and include your primary keyword.
- Craft clear, accurate title tags (~60 characters) that tell users and search engines what the page is about.
- Use Open Graph (OG) and Twitter Card tags so your content renders properly when shared across platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and X.
- Ensure mobile usability, including responsive layouts, tappable buttons, and minimal horizontal scrolling.
- Use readable fonts and clean formatting, especially for body copy, to reduce bounce and improve time on page.
- Adhere to accessibility guidelines, such as:
- Sufficient color contrast between text and background
- Alt text for all images, describing content clearly and concisely
- Descriptive link text (avoid “click here”)
- Proper use of headings (H1, H2, H3) for screen reader hierarchy
- ARIA labels where applicable
Example: A healthcare system publishing a guide to managing diabetes should not only optimize its title and meta description for search queries like “how to manage type 2 diabetes,” but also ensure that the content is accessible for low-vision users, includes properly tagged charts or images, and renders flawlessly on mobile devices. This improves patient engagement, helps AI trust the page, and boosts discoverability across platforms.
10. Refresh, Update, and Monitor
AI is not static—and neither is the way your content gets surfaced, interpreted, or prioritized. New terminology emerges, regulations shift, user behavior evolves, and AI models continuously retrain on fresh data. That means your high-performing content today could quietly slip into irrelevance if it isn’t maintained.
To stay visible in AI Overviews, featured snippets, and traditional rankings, your content needs a proactive maintenance plan. Treat every page as an evolving product—not a set-it-and-forget-it project.
Why It Matters:
- AI models prioritize freshness. Pages with up-to-date facts, current terminology, and recent updates are more likely to be seen as trustworthy sources.
- User trust is tied to accuracy. Outdated stats or broken links don’t just hurt your SEO—they damage your brand’s credibility.
- Your competitors are catching up. If you stood out once, others are likely replicating your strategy. Iteration is your edge.
Best Practices:
- Conduct quarterly or biannual content audits. Look for outdated references, missing CTAs, broken links, obsolete screenshots, or changes in terminology.
- Update stats, charts, and citations with recent data. Replace “as of 2022” references with “2024” and update links to newer studies or sources.
- Add new internal links. Link to newer content that wasn’t available when the original article was published to help reinforce authority and recirculate traffic.
- Watch for AI summarization trends. AI tools are citing shorter, cleaner, more structured answers. Consider refining your content layout to match this pattern.
- Review SERP competitors regularly. Who’s ranking above you now? What have they done differently? Borrow structure or topical improvements where relevant.
Tool Tip:
Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test, Search Console Insights, and Bing Webmaster Tools to see which pages are gaining traction—and which need work. If you have access to Google’s Search Generative Experience, monitor AI Overviews for your target terms to see if your brand is showing up or being skipped. When it’s not, that’s your cue to revise, strengthen, or reposition.
Example: A cybersecurity firm might review its core resources every quarter, updating terminology from “multi-factor authentication” to “passkeys,” revising threat data, and inserting links to new blog posts about recent exploits. Screenshots showing outdated UI should be swapped for current ones. These small updates signal freshness and help content stay relevant in AI citation graphs and search engine rankings.
Final Word on AI SEO Strategies: Design for AI, Deliver for People
AI-friendly content isn’t artificial—it’s intentional. It’s designed to help people and algorithms understand, trust, and share your message. By structuring your content clearly, layering in multimedia, showcasing real authority, and distributing insight across platforms, you can shape how the internet—and AI—remembers you.
Whether you’re recruiting franchisees, landing manufacturing contracts, or educating clients on complex tax law, these strategies give your brand the edge in today’s search landscape.
Time is the most unforgiving factor in the evolving landscape of AI-driven search. As AI Overviews increasingly dominate search results—appearing in over 40% of SERPs as of April 2025—the window to establish your brand’s authority is narrowing. Our foundational article, How to Optimize Content to Rank in AI Search Results, underscores the urgency of adapting to these changes. Without a robust, forward-thinking AI SEO strategy, internal teams may find themselves outpaced by competitors who have already secured their positions in AI-generated content.
To understand the investment required for effective SEO, refer to How Much Does It Cost to Hire an SEO Company in 2025?. This article provides a detailed breakdown of SEO investment levels, helping you comprehend the costs associated with various service tiers.
For insights into how SEO professionals can optimize your content for AI-driven search engines, explore How Does an SEO Expert Help You Rank in AI Search Results?. This resource explains the strategies employed by SEO experts to ensure your business remains visible in the evolving digital landscape.
At Xponent21, we’re leaders in crafting and executing comprehensive AI SEO strategies that not only keep you in the race but position you to lead. Don’t let the rapid evolution of search leave your brand behind—contact us to take decisive action today.

